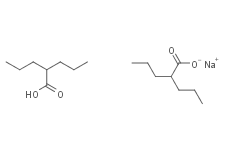
Divalproex Sodium
CAS No. 76584-70-8
Divalproex Sodium( —— )
Catalog No. M19090 CAS No. 76584-70-8
Divalproex Sodium binds to and inhibits gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transaminase and its anticonvulsant activity may be exerted by increasing brain concentration of GABA and by inhibiting enzymes that catabolize GABA or block the reuptake of GABA into glia and nerve endings.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 106 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 178 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDivalproex Sodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDivalproex Sodium binds to and inhibits gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transaminase and its anticonvulsant activity may be exerted by increasing brain concentration of GABA and by inhibiting enzymes that catabolize GABA or block the reuptake of GABA into glia and nerve endings.
-
DescriptionDivalproex Sodium binds to and inhibits gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transaminase and its anticonvulsant activity may be exerted by increasing brain concentration of GABA and by inhibiting enzymes that catabolize GABA or block the reuptake of GABA into glia and nerve endings. It also is an HDAC inhibitor. Divalproex Sodium is a stable coordination compound comprised of sodium valproate and valproic acid with anticonvulsant and antiepileptic activities. Divalproex may also work by suppressing repetitive neuronal firing through inhibition of voltage-sensitive sodium channels.(In Vitro):Valproic acid (VPA) (0-15 mM; 24 and 72 h) inhibits Hela cell growth in a dose- and time- dependent manner.Valproic acid (10 mM; 24 h) significantly attenuates the activities of total, cytosol and nuclear HDACs.Valproic acid (0-15 mM; 24 h) induces a G1 phase arrest at 1–3 mM and a G2/M phase arrest at 10 mM, and increases the percentage of sub-G1 cells in HeLa cells. Valproic acid also induces necrosis, apoptosis and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release.Valproic acid (0-20 mM; 24 h) activates Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription and synergizes with lithium.Valproic acid (0-5 mM; 0-18 h) increases β-catenin levels in Neuro2A cells.Valproic acid (0-2 mM; 0-24 h) stimulates phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC in hepatocytes.Valproic acid (0-10 mM; 2 days) induces Notch1 signaling and morphologic differentiation, suppresses production of NE tumor markers in SCLC cells.(In Vivo):Valproic acid (VPA) (500 mg/kg; i.p.; daily for 12 days) inhibits tumor angiogenesis in mice transplanted with Kasumi-1 cells.Valproic acid (350 mg/kg; i.p.; once) enhances social behavior in rats.Valproic acid (0.26% (w/v); p.o. via drinking water; 14 days) decreases liver mass, hepatic fat accumulation, and serum glucose in obese mice without hepatotoxicity.
-
In VitroValproic acid (VPA) (0-15 mM; 24 and 72 h) inhibits Hela cell growth in a dose- and time- dependent manner.Valproic acid (10 mM; 24 h) significantly attenuates the activities of total, cytosol and nuclear HDACs. Valproic acid (0-15 mM; 24 h) induces a G1 phase arrest at 1–3 mM and a G2/M phase arrest at 10 mM, and increases the percentage of sub-G1 cells in HeLa cells. Valproic acid also induces necrosis, apoptosis and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release.Valproic acid (0-20 mM; 24 h) activates Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription and synergizes with lithium.Valproic acid (0-5 mM; 0-18 h) increases β-catenin levels in Neuro2A cells.Valproic acid (0-2 mM; 0-24 h) stimulates phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC in hepatocytes.Valproic acid (0-10 mM; 2 days) induces Notch1 signaling and morphologic differentiation, suppresses production of NE tumor markers in SCLC cells. Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:HeLa cells Concentration:0, 1, 3, 5, 10 and 15 mM Incubation Time:24 and 72 h Result:HeLa cell growth was dose- and time-dependently decreased with an IC50 of ~10 and 4 mM at 24 and 72 h.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:HeLa cells, Neuro2A cells or primary mouse hepatocytes Concentration:10 mM (HeLa); 0, 2, and 5 mM (Neuro2A); 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2 and 2 mM (hepatocytes)Incubation Time:24 h (HeLa); 0-18 h (Neuro2A); 0-24 h (hepatocytes) Result:Increased the form of acetylated histone 3. Reduced PARP, induced cleavage PARP, and downregulated Bcl-2. Increased β-catenin levels. Increased the phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC.Cell Cycle Analysis Cell Line:HeLa cells Concentration:0, 1, 3, 5, 10 and 15 mM Incubation Time:24 h Result:Induced a G1 phase arrest at 1–3 mM, significantly induced a G2/M phase arrest at 10 mM, and increased the percentage of sub-G1 cells in HeLa cells in a dose-dependent manner at 24 h.
-
In VivoValproic acid (VPA) (0-15 mM; 24 and 72 h) inhibits Hela cell growth in a dose- and time- dependent manner.Valproic acid (10 mM; 24 h) significantly attenuates the activities of total, cytosol and nuclear HDACs. Valproic acid (0-15 mM; 24 h) induces a G1 phase arrest at 1–3 mM and a G2/M phase arrest at 10 mM, and increases the percentage of sub-G1 cells in HeLa cells. Valproic acid also induces necrosis, apoptosis and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release.Valproic acid (0-20 mM; 24 h) activates Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription and synergizes with lithium.Valproic acid (0-5 mM; 0-18 h) increases β-catenin levels in Neuro2A cells.Valproic acid (0-2 mM; 0-24 h) stimulates phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC in hepatocytes.Valproic acid (0-10 mM; 2 days) induces Notch1 signaling and morphologic differentiation, suppresses production of NE tumor markers in SCLC cells. Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:HeLa cells Concentration:0, 1, 3, 5, 10 and 15 mM Incubation Time:24 and 72 h Result:HeLa cell growth was dose- and time-dependently decreased with an IC50 of ~10 and 4 mM at 24 and 72 h.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:HeLa cells, Neuro2A cells or primary mouse hepatocytes Concentration:10 mM (HeLa); 0, 2, and 5 mM (Neuro2A); 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2 and 2 mM (hepatocytes)Incubation Time:24 h (HeLa); 0-18 h (Neuro2A); 0-24 h (hepatocytes) Result:Increased the form of acetylated histone 3. Reduced PARP, induced cleavage PARP, and down regulated Bcl-2. Increased β-catenin levels. Increased the phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC.Cell Cycle Analysis Cell Line:HeLa cells Concentration:0, 1, 3, 5, 10 and 15 mM Incubation Time:24 h Result:Induced a G1 phase arrest at 1–3 mM, significantly induced a G2/M phase arrest at 10 mM, and increased the percentage of sub-G1 cells in HeLa cells in a dose-dependent manner at 24 h.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorHDAC
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number76584-70-8
-
Formula Weight310.41
-
Molecular FormulaC8H16O2·C8H15O2·Na
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES[Na+].CCCC(CCC)C(O)=O.CCCC(CCC)C([O-])=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Wang W, et al. Cancer Lett, 2015, 356(2 Pt B), 791-799.
molnova catalog



related products
-
1,3-Dimethylpyrazole
1,3-Dimethylpyrazole is a bioactive compound isolated from Moso Bamboo Root.
-
Pyrrolidine
Pyrrolidine is a flavoring agent which could be found in the leaves of tobacco and carrot.
-
TN-16
TN-16 is a microtubule polymerization inhibitor?(IC50 :0.4-1.7 μM).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


